MỤC LỤC BÀI VIẾT
Introduction
In the world of construction, carpentry, and industrial manufacturing, industrial nails play a crucial role in ensuring structural integrity and efficient production. Among various types of nails, coil nails have emerged as a popular and highly practical solution for both large-scale production lines and onsite construction work. Known for their versatility, efficiency, and durability, coil nails are used in everything from building wooden pallets to framing houses.
This article provides an in-depth look at coil nails—what they are, how they’re made, their types, benefits, and the industries that rely on them. Whether you’re a builder, manufacturer, or supplier, understanding coil nails will help you choose the right fasteners for your applications and improve your productivity and cost-efficiency.

What Are Coil Nails?
Coil nails are a type of collated nail arranged in a spiral formation and connected by wire or plastic strips. These nails are stored in coils and loaded into a pneumatic nail gun or coil nailer, allowing the user to rapidly and continuously drive nails without frequent reloading.
A single coil can hold between 1800 to 9000 nails, depending on the nail size and gauge, making them highly efficient for continuous use in industrial or commercial environments.
Key Components of a Coil Nail
Each coil nail is composed of three essential parts:
Head:
The top of the nail, which may be full round, clipped, or offset. Full round heads offer better holding power, especially in framing and roofing.Shank:
The body of the nail, which comes in several forms:Smooth shank: Easy to drive but provides less holding power.
Ring shank: Features ridges for strong grip in wood, ideal for resisting withdrawal.
Spiral or Screw shank: Twisted design increases holding power by rotating as it’s driven.
Point:
The tip of the nail, often diamond-shaped or blunt. The point design affects how easily the nail penetrates the material and whether it minimizes wood splitting.
Manufacturing and Materials
Coil nails are typically made from carbon steel, although stainless steel options are available for highly corrosive environments. To increase longevity, manufacturers often apply coatings such as:
Bright finish: Untreated nails for indoor use.
Vinyl coating: Helps reduce driving resistance and adds moderate corrosion resistance.
Galvanized (electro or hot-dip): Offers protection against rust, ideal for outdoor or humid conditions.
Epoxy or polymer coatings: Specialized coatings for added durability and environmental resistance.
Types of Coil Nails
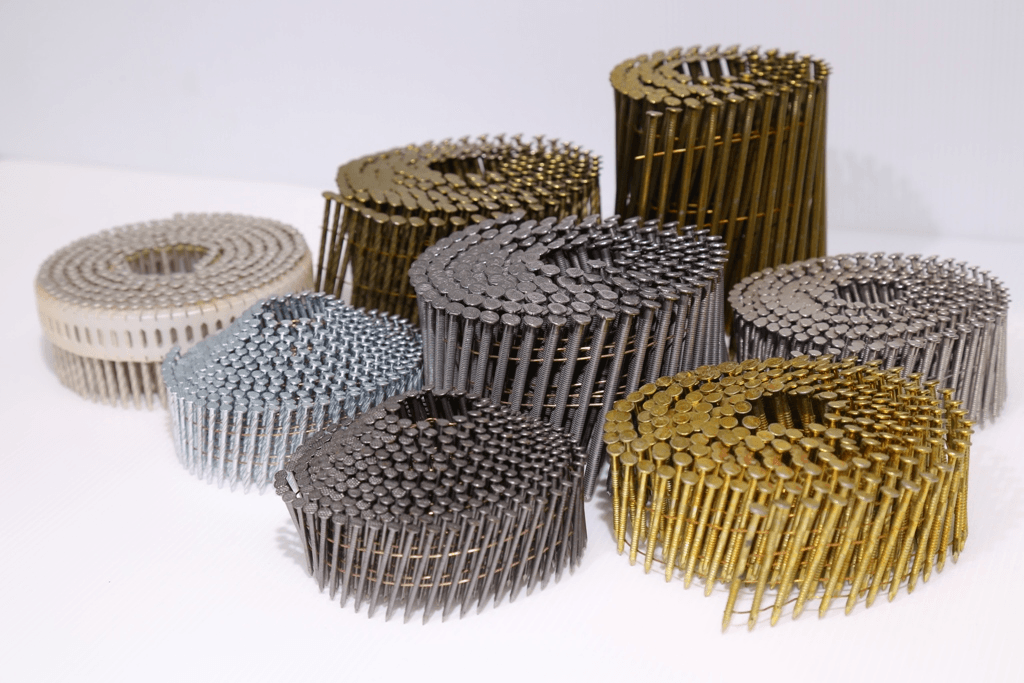

By Angle and Collation
Coil nails are typically collated at a 15-degree angle, although variations exist (16°, 20°, etc.) depending on the tool manufacturer.
The two main collation types are:
Wire Collated: Nails are held together with thin wires—durable and heat resistant.
Plastic Collated: More common in certain regions.
By Application
Roofing Coil Nails
Short, wide-head nails designed for attaching shingles and roofing materials.Framing Coil Nails
Longer, heavy-duty nails used in structural framing and wood joining.Siding Coil Nails
Designed with smaller heads or rings to reduce visibility and hold siding materials securely.Pallet Coil Nails
Ideal for high-speed pallet and crate manufacturing—these nails are optimized for consistent performance on industrial lines.Drywall and Sheathing Nails
Engineered to prevent material damage while securing panels in place.
Technical Specifications
Here are some common specifications of coil nails:
| Parameter | Typical Range |
|---|---|
| Length | 1” to 4” (25mm to 100mm) |
| Diameter | 0.080” to 0.148” (2.0mm to 3.8mm) |
| Coil Type | Wire or Plastic Collated |
| Collation Angle | 15° (most common) |
| Coil Capacity | 1800 – 9000 nails per coil |
| Shank Types | Smooth, Ring, Spiral |
| Head Styles | Full Round, Clipped, Offset |
| Finish Options | Bright, Vinyl, Galvanizedl |
Advantages of Coil Nails
1. High Efficiency
The large capacity of a coil (up to 1300 nails) minimizes reloading, allowing workers to focus on the job and reduce downtime.
2. Stronger Holding Power
When paired with the right shank type, coil nails offer excellent holding strength, especially important in high-stress applications like framing or palletizing.
3. Consistent Quality and Placement
Coil nails are manufactured with strict tolerances, resulting in consistent size, spacing, and alignment. This consistency leads to cleaner, more professional finishes.
4. Reduced Jamming and Tool Wear
High-quality coil nails are less likely to jam in nail guns, reducing maintenance costs and extending the life of your tools.
5. Compact and Easy to Store
Coils are space-efficient and easy to transport. Multiple coils can be stored in a small area, making them ideal for job sites with limited space.
Applications Across Industries
Coil nails are used across a wide range of sectors:
1. Construction and Framing
Used for framing walls, roofing, decking, sheathing, and subfloors. Their strong grip and fast installation make them indispensable in residential and commercial building projects.
2. Pallet and Crate Manufacturing
In high-volume environments, such as pallet factories, coil nails are the standard. Their speed and reliability make them perfect for automated nailing systems.
3. Furniture and Cabinetry
For quick assembly of furniture frames or backs, especially when using soft or engineered woods.
4. Siding and Fencing
Specialized coil nails for siding provide the corrosion resistance and appearance needed for exterior wood paneling or fencing.
5. DIY and Home Renovation
More advanced DIYers use coil nails with portable pneumatic nailers for remodeling, decking, and roofing projects.
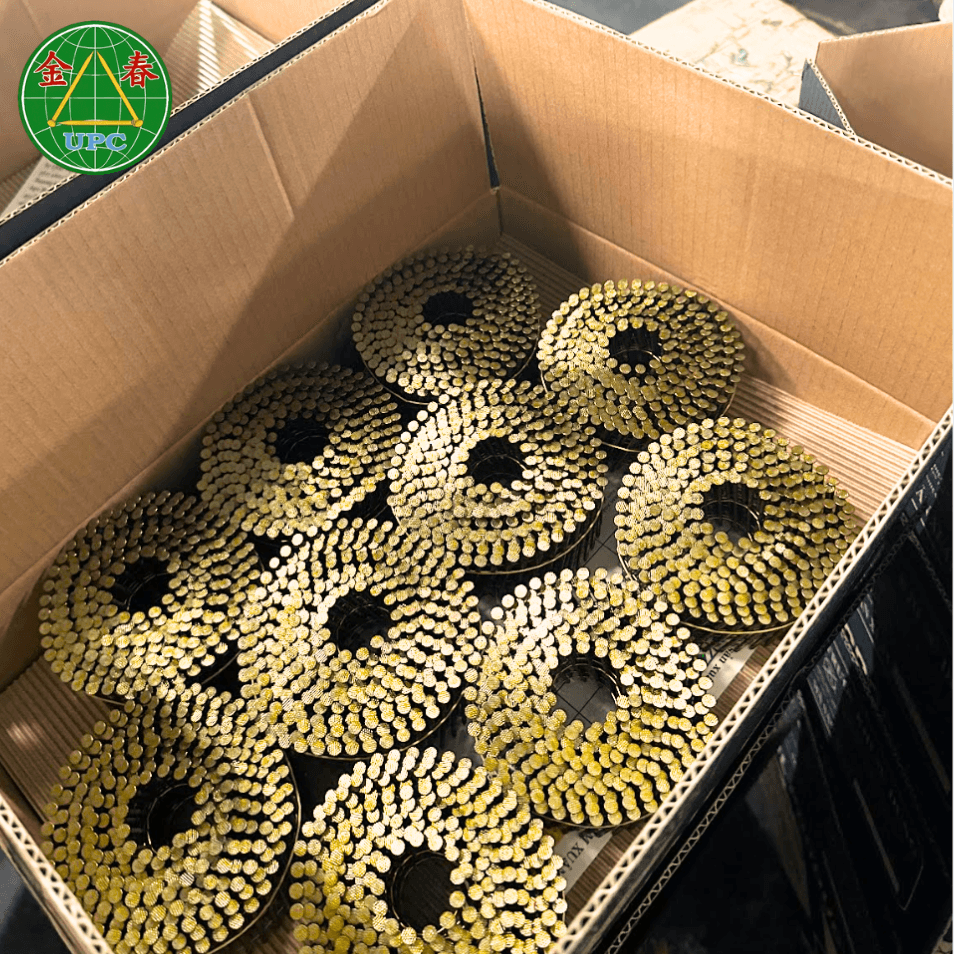
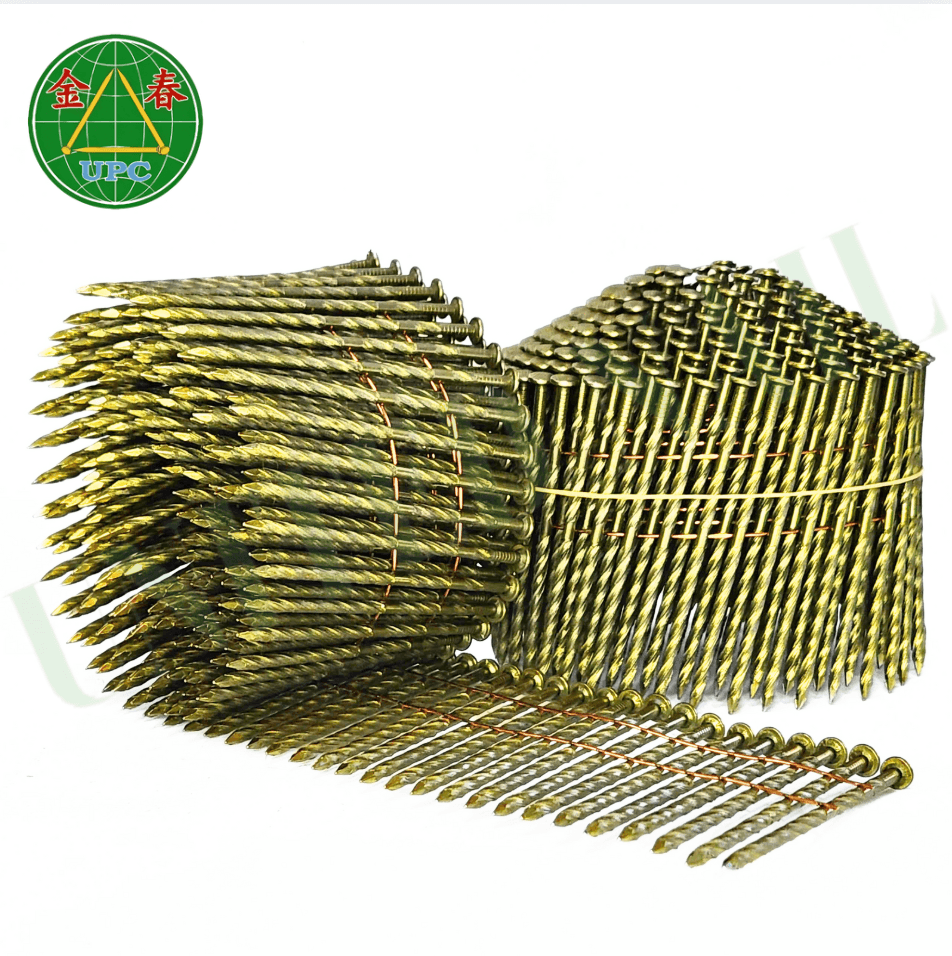


How to Choose the Right Coil Nail
When selecting coil nails, consider the following:
Application: Are you framing, roofing, or building pallets?
Material: Use stainless steel or hot-dip galvanized nails for outdoor or moisture-prone environments.
Tool Compatibility: Ensure the coil matches the angle and feed mechanism of your nail gun.
Holding Power Needs: Choose the correct shank (ring or spiral) if withdrawal resistance is important.
Regulations and Certifications: In some regions or projects, nails must comply with specific construction codes or standards (e.g., ASTM, CE, ISO).
Best Practices for Use
Store coil nails in a dry area to avoid corrosion.
Avoid using non-galvanized nails in exterior projects.
Match the nail’s length to the material thickness—standard rule is the nail should penetrate the base at least 1 to 1.5 inches.
Regularly clean and inspect nailers to avoid jamming or misfires.
Conclusion
Coil nails are a cornerstone of modern fastening technology, offering a blend of speed, strength, and convenience that few other solutions can match. Whether you’re a construction professional, pallet manufacturer, or hardware distributor, using the right coil nail product can drastically improve operational efficiency and ensure long-lasting, reliable results.
As industries increasingly demand faster production with fewer errors, coil nails—especially in coils of 1800–9000 nails—are the go-to choice for maximizing productivity without sacrificing quality.
For premium coil nails in various specifications, finishes, and packaging options, reach out to reputable manufacturers who can provide tailored solutions for your specific application.
Contact Information
UNITED NAIL PRODUCTS CO., LTD
Specializing in high-quality nails and small coil wire production
Thank you for taking the time to read this article. We hope the information proves helpful to you.